The comparison npn vs pnp transistors It is important to understand how bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) behave in real electronic circuits. Although NPN and PNP transistors have the same basic function—using a small control current to regulate a larger current—their internal structure, bias logic, current direction, and application scenarios differ in several ways.
These differences directly affect schematic design, component selection, PCB layout, grounding strategy, and even system-level safety behavior. Engineers who understand clearly npn vs pnp can create cleaner designs, avoid common wiring errors, and improve long-term reliability in both analog and digital systems.
What is an NPN Transistor?
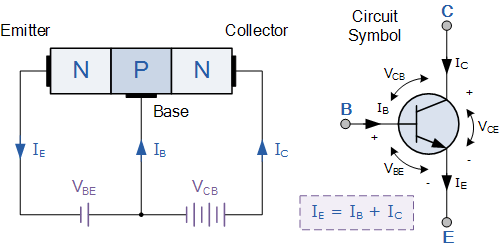
A NPN transistors is a type of bipolar junction transistor made of three semiconductor regions arranged as follows N-type emitter, P-type base and N-type collector. The name “NPN” reflects this physical structure.
In NPN transistors:
- electron is the majority charge carrier
- The emitter is heavily doped to inject electrons
- The base is thin and lightly doped
- The collector collects electrons flowing through the device
Because electrons move faster than holes, NPN transistors generally offer better switching speeds and higher gain than PNP devices. This is one of the main reasons why NPN transistors dominate modern electronic design.
How Does an NPN Transistor Work?
NPN transistors operate with forward biases the base-emitter junction. When the base voltage is increased approximately 0.7 V above the emitter (for silicon devices), electrons begin to flow from the emitter to the base.
Most of these electrons do not recombine in the base. Instead, they are drawn into the collector by the collector base electric field. As a result:
- A small base current control
- A the collector current is much larger
This behavior allows the NPN transistor to function as:
- Current amplifier
- A digital switch
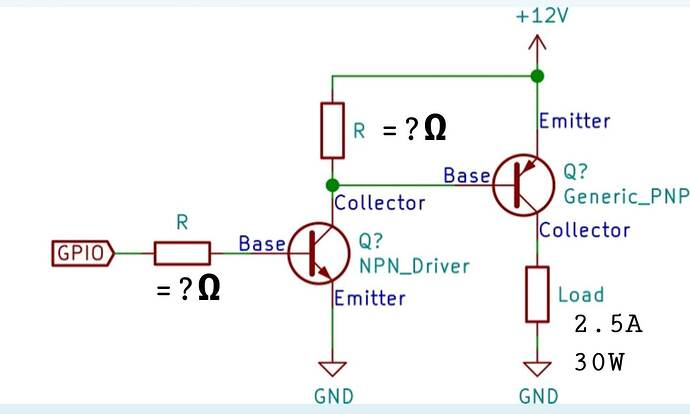
In PCB applications, NPN transistors are most often used as low side switchwhere the load is connected to the supply voltage and the transistor completes the path to ground.
Advantages and Limitations of NPN
Advantages of NPN Transistors
- Faster switching due to electron mobility
- Simple bias with logic that refers to basics
- Excellent compatibility with microcontrollers and digital ICs
- Wide availability in signal, power and RF variants
- Lower cost at most voltage and current ratings
Limitations of NPN Transistors
- Not ideal for high side switching without level switching
- Ground noise can affect sensitive analog stages
- The load remains connected to the supply when the transistor is off
What is a PNP Transistor?
A PNP transistors is also a bipolar junction transistor, but the internal structure is reversed: P-type emitter, N-type base and P-type collector.
In PNP transistors:
- hole is the majority charge carrier
- Current flows from the emitter to the collector
- Inverted control logic compared to NPN
PNP transistors are generally used when the design requires switching or controlling current on positive side of the power supply.
How Does a PNP Transistor Work?
The PNP transistor turns on when base voltage is lower than emitter voltage about 0.7 V. This provides a forward bias at the base-emitter junction and allows the hole to move from the emitter to the base.
Once active:
- The hole continues into the collector
- Current flows from emitter → collector → load
Because of this current direction, PNP transistors are very suitable for use high side switchwhere the transistor supplies current from the power rail to the load.
Advantages and Limitations of PNP
Advantages of PNP Transistors
- The natural solution to high side switching
- Useful in power distribution and source circuits
- Allows the load to be completely disconnected from the supply
- Common in automotive and industrial controls
Limitations of PNP Transistors
- Switching is slower due to hole mobility
- Less intuitive control logic for beginners
- It is more difficult to interact directly with low voltage logic
- Often requires a pull-down or level-shifting circuit
NPN vs PNP Symbols: How to Identify Them?
The transistor symbol provides a clear visual clue:
- NPN transistors: emitter arrow point go out
- PNP transistors: emitter arrow point inner
Commonly used memory aids are:
“NPN: Not Pointing inward.”
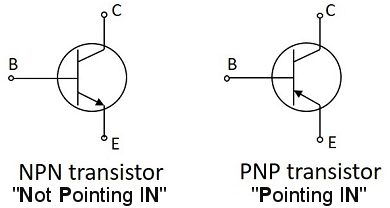
Correctly identifying transistor symbols is critical during schematic review and PCB trace validation, especially when layouts are shared across teams.
Why Do You Use PNP Transistors?
You would choose a PNP transistors when the design requires:
- Turning on positive supply rail
- Default dead load when the control signal is not active
- Current sources, rather than sinks
- Simplified high side power control
PNP transistors are often used in:
- Automotive electronics
- Industrial automation
- Power monitoring circuit
- Sensor supply control
Key Differences Between NPN and PNP Transistors
| Aspect | NPN transistors | PNP transistors |
| Semiconductor structure | NPN | PNP |
| Majority operators | electron | hole |
| Power on condition | The base is higher than the emitter | The base is lower than the emitter |
| Current flow | Collector → Emitter | Emitter → Collector |
| Typical role | Low side switch | High side switch |
| Logical compatibility | Very good | More complex |
When to Use NPN vs PNP Transistors?
Choose npn vs pnp depending on the system architecture and control logic:
- Use NPN when working with microcontrollers, logic ICs, or ground reference signals
- Use PNP when switching the load from the positive rail
- Consider PCB grounding, noise paths, and return current
- Evaluate system behavior during startup and fault conditions
In advanced designs, NPN and PNP transistors are often paired in complementary stages to achieve push-pull, level-shifting, or bidirectional drive output.
FAQs
1. Are NPN transistors better than PNP transistors?
Nothing is universally better. NPN is more common, while PNP excels at high side control.
2. Can NPN and PNP transistors be used together?
Yes. Many amplifiers and drivers rely on complementary NPN/PNP pairs.
3. Why are NPN transistors used more often?
They switch faster, are cheaper, and easily interface with logic circuits.
4. How to identify NPN vs PNP on PCB?
Check schematic symbols, component markings, or datasheet pinouts.
5. Can I directly replace the PNP transistor with an NPN transistor?
No. The current bias and direction are different and require redesign.
Tag: npn vs pnp transistor, npn vs pnp transistor
This entry was posted on Friday, January 16, 2026 at 09:42 and is filed under best PCB, best PCB, FAQ, PCBA. You can follow any responses to this entry via the RSS 2.0 feed. You can skip to the end and leave a response. Ping is currently not allowed.
News
Berita Teknologi
Berita Olahraga
Sports news
sports
Motivation
football prediction
technology
Berita Technologi
Berita Terkini
Tempat Wisata
News Flash
Football
Gaming
Game News
Gamers
Jasa Artikel
Jasa Backlink
Agen234
Agen234
Agen234
Resep
Download Film
Gaming center adalah sebuah tempat atau fasilitas yang menyediakan berbagai perangkat dan layanan untuk bermain video game, baik di PC, konsol, maupun mesin arcade. Gaming center ini bisa dikunjungi oleh siapa saja yang ingin bermain game secara individu atau bersama teman-teman. Beberapa gaming center juga sering digunakan sebagai lokasi turnamen game atau esports.
Comments are closed, but trackbacks and pingbacks are open.