In any case RF PCB material used for wireless modules, radar systems, or 5G designs, only a few parameters impact performance strongly DKor dielectric constant. When engineers talk about it controlled impedance PCB structureDK is at the heart of every decision. This shapes signal speed, impedance behavior, and even how your RF transmission lines behave at microwave frequencies.
If your goals are stable and predictable high frequency PCB designunderstanding why DK is important will help you choose a better laminate and avoid expensive setup steps.
DK Directly Determines RF Transmission Line Impedance
Every RF microstrip impedance calculation Depends on DK. The dielectric constant of the material is entered into a formula that determines the final impedance for 50Ω microstrip lines, 75Ω video lines, and many special RF structures.
The relationship is simple:
- Higher DK → lower impedance
- Lower DK → higher impedance
Here’s why RF PCB stack design can only be accurate if the underlying DK is consistent. Even a small DK shift, such as ±0.1, can move the impedance by a few ohms. At microwave frequencies, these differences affect return loss, matching accuracy, and filter or antenna stability.
To reduce this variation, engineers often choose Rogers RF Materials such as RO3003, RO4003C, and RO4350B, which maintain tighter DK tolerances than conventional FR4.
DK Stability Protects RF Circuits From Impedance Deviations
Standard materials, such as FR4, exhibit large DK swings at different frequencies and temperatures. But advanced high frequency laminate materials are designed for stability against changes in environment, humidity and frequency range.
Stable DK provides stable impedance, leading to:
- cleaner signal flow
- predictable matching in RF front-end circuitry
- stable phase length for microwave structures
- consistent PCB RF Routing show
For microwaves, especially above 2–3 GHz, DK tolerance becomes one of the clearest indicators of high quality RF PCB material selection.
DK Controls RF Signal Propagation
Impedance isn’t just a number—it reflects how electromagnetic energy moves across the PCB. DK defines the relationship between the electric field in the trace and the dielectric beneath it. When DK is stable, the signal propagation speed also remains stable.
This affects many RF structures:
- microstrip antenna
- transmission lines for mixer, LNA, and PA
- VCO and PLL circuit
- bandpass filter and coupler
- phased array elements
- radar transmitter path
With a stable DK, the structure behaves close to the modeled performance, thereby reducing the risk of frequency drift or unexpected resonance shifts.
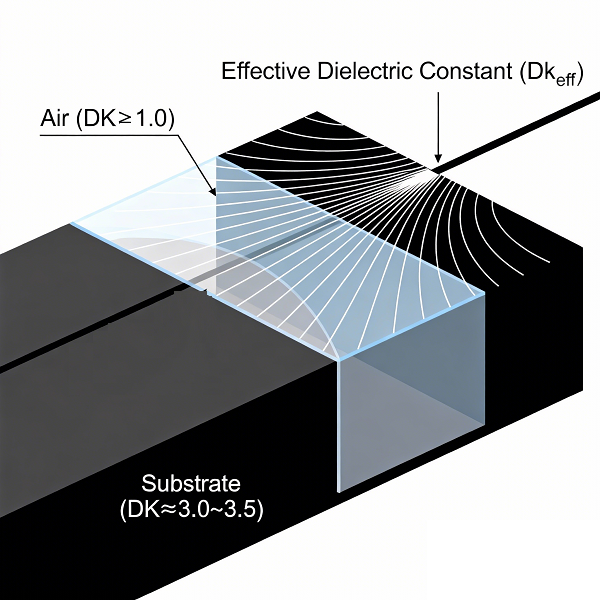
DK Affects Effective Permissions (Dk_eff)
Most RF layouts use grounded microstrip or CPW traces, where only part of the electromagnetic field flows within the medium. The remaining fields propagate through the air. The combined effect is called Effective dielectric constant (εeff) or Dk_eff.
Since Dk_eff is between the DK of the substrate and the DK of the air (≈1.0), any movement in the DK of the substrate will shift the effective value.
This creates changes to:
- impedance
- phase speed
- length of power line
- signal wavelength on the PCB
- connector between adjacent structures
For this reason, Impedance controlled PCB for RF applications requires laminates with tight DK tolerances throughout the panel and throughout the RF array.
Tight DK Tolerances Reduce Prototyping Time
When using predictable materials, the simulation model better matches the actual PCB results. Designers experience fewer setup cycles, fewer redesigns, and faster production.
Consistent DK helps:
- improve RF throughput
- reduces the adjustment on the power amplifier bias line
- recurring support RF PCB Manufacturing
- makes stack calculations more accurate
This is especially valuable in industries such as automotive radar, satellite communications, low-noise amplifier design, and compact 5G modules.
DK Variations Increase Reflection and Mismatch Loss
The loss tangent (Df) defines the dielectric losses, but variations in DK give rise to mismatch loss. When the impedance deviates from the desired value, some of the RF signal is reflected back to the source, thereby reducing forward transmission.
Effects include:
- higher insertion loss
- increased ripple in the filter
- VSWR is degraded
- phase error in the antenna array
- unwanted standing waves
Stable DK helps avoid this problem by keeping the impedance as close to the original design target as possible.
DK and RF PCB Stacking Selection
High performance RF PCB stack design always starts with DK. Engineers set the thickness of the copper, the thickness of the dielectric, and trace the surrounding geometry. RF stacks with predictable DK behave consistently across production batches, keeping high volume runs stable.
Popular RF materials selected for stabilized DK include:
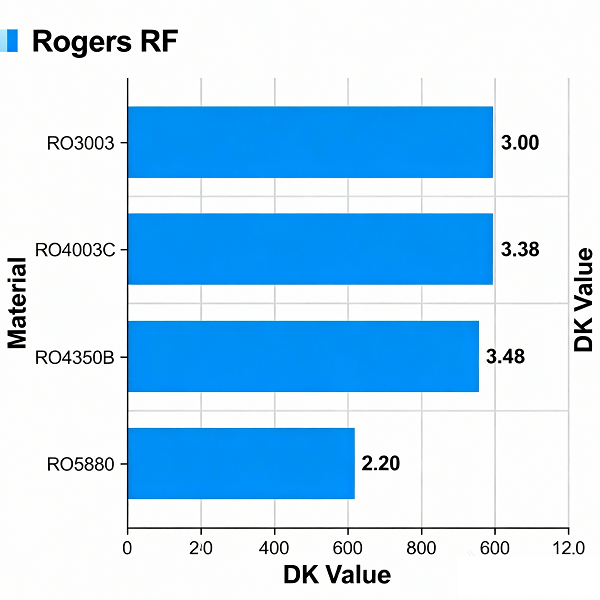
- Rogers RO3003 (DK ≈ 3.00 ± 0.04)
- Rogers RO4350B (DK ≈ 3.48 ± 0.05)
- Rogers RO4003C (DK ≈ 3.38 ± 0.05)
- Rogers RO5880 (DK ≈ 2.20 ± 0.02)
- Taconic RF-35, TLY, and other PTFE based laminates
This laminate is widely used in microwave design because it gives designers confidence that electrical impedance and length remain predictable throughout the building.
Why is DK More Important Above 10 GHz?
When the frequency expands into the mmWave range, small DK deviations cause large impedance shifts. The higher the operating frequency, the more sensitive the impedance is to variations in the dielectric constant.
For example:
- At 1–2 GHz, a DK tolerance of ±0.05 produces a measurable but manageable impact.
- At 10–24 GHz, the same DK deviation causes a more dramatic impedance change.
- Above 28–39 GHz (5G FR2 band), DK control becomes one of the most important parameters in RF material selection.
Here’s why mmWave PCB manufacturing relies heavily on PTFE or ceramic based laminates with very tight DK tolerances.
Best Technology – Your Trusted Partner for RF PCB Manufacturing
For designers working on high frequency and microwave projects, proper DK control is just the starting point. You also need a PCB manufacturer with strong RF engineering experience, a stable process, and a deep understanding of manufacturing impedance-controlled PCBs. On Best Technologywe support the global RF team through:
1. Advanced RF PCB materials – RO3003, RO4350B, RO4003C, RO5880, Taconic and other high frequency laminates.
2. Tight impedance tolerance – ±5% impedance control with certified test report.
3. Professional RF stack design assistance – Our engineers help calculate trace width, dielectric thickness and Dk_eff model for accurate impedance.
4. Mature RF PCB fabrication capabilities – Microstrip, stripline, CPW, grounded CPW, hybrid stack, cavity structure and metal-backed RF boards.
5. Strict quality control – ISO9001, ISO13485, AS9100D, IATF16949 and full MES traceability for all builds.
When your RF design demands precise signal behavior, stable impedance, and reliable material performance, Best Technology provides the expertise and manufacturing power needed to support advanced RF and microwave innovation.
Tags: controlled impedance PCB, high frequency PCB design, rf PCB materials, RF PCB stack design, Rogers RF materials
This entry was posted on Thursday, December 11, 2025 at 18:48 and is filed under best PCB, best PCB, FAQ, RF Board. You can follow any responses to this entry via the RSS 2.0 feed. You can skip to the end and leave a response. Ping is currently not allowed.
News
Berita Teknologi
Berita Olahraga
Sports news
sports
Motivation
football prediction
technology
Berita Technologi
Berita Terkini
Tempat Wisata
News Flash
Football
Gaming
Game News
Gamers
Jasa Artikel
Jasa Backlink
Agen234
Agen234
Agen234
Resep
Download Film
Gaming center adalah sebuah tempat atau fasilitas yang menyediakan berbagai perangkat dan layanan untuk bermain video game, baik di PC, konsol, maupun mesin arcade. Gaming center ini bisa dikunjungi oleh siapa saja yang ingin bermain game secara individu atau bersama teman-teman. Beberapa gaming center juga sering digunakan sebagai lokasi turnamen game atau esports.
Comments are closed, but trackbacks and pingbacks are open.